The Digital health breakthrough
The Covid-19 pandemic has reshaped every aspect of our lives, from our education system to social interactions, but nothing has seen as much growth as the medical and digital health fields.
From the start of the pandemic, E-health had a major rise in popularity since people who were sick or injured still needed to be seen by doctors but wanted to avoid going in person to avoid the coronavirus.
Telemedicine is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to innovations in E-health. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Virtual Reality (VR) have redefined how we can diagnose and treat patients remotely, and we have only scratched the surface of what these technologies can do.
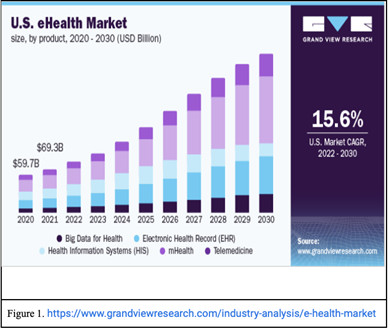
As seen in Figure 1 below, the US E-health market was valued at $69.3 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow rapidly with a CAGR of 15.6% by the year 2030.
With the popularity of contactless options in the wake of the pandemic, the E-Health field has ample opportunity to expand and grow in the coming years.
Trends in Telemedicine
Before February 2020, telemedicine had limited capacity, and while it was gaining traction, it was not predicted to become such a large part of the healthcare industry suddenly.
With the pandemic came a necessity to change how traditional healthcare functions over a short period of time. Overfilled hospitals and public reservations for in-person visits caused a major push to move doctor appointments virtually when possible.
After a large spike following the pandemic’s start, telemedicine usage stabilized at 38 times what it was pre-pandemic.
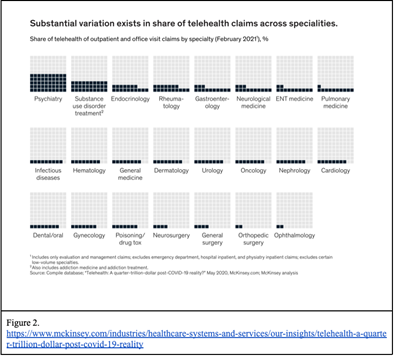
While telehealth is limited to appointments that do not need physical evaluation, the industry has utilized telehealth post-pandemic for more than two-thirds of what was anticipated by Mckinsey & Company (figure 2).
Telehealth has changed how patients receive healthcare, and the innovation of predictive technologies that patients can access from their personal devices will cause unprecedented growth in the telehealth industry. This change has already begun, as wearable devices, connected biometric sensors, sophisticated home monitoring instruments, and smartphone cameras have all been introduced to users at home in recent years.
In the following sections, we will discuss how Machine Learning (ML) is used in healthcare and how it will continue to transition from professional use to home use in the coming years.
Innovations in Predictive Medicine
Predictive medicine has seen major advancement over the years as new technologies have been integrated into the field.
Machine learning is a major driver in the growth of this field, as algorithms can pick up on patterns and, by using AI tools, can help predict diseases and suggest immediate treatments that can help slow down or cure these medical conditions.
Software as a medical device
Machine learning and artificial intelligence can be integrated into Software as Medical Device (SaMD) tools to bring this technology to patients. The SaMD can be a stand-alone or a decision-support tool for physicians.
Defined by the International Medical Device Regulators Forum, Software as a Medical Device is “software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.”
SaMD includes a wide range of technologies from software programmed onto smartphones to Computer-Aided Detection medical software. This software can also be included in other hardware medical devices as a SiMD (Software in Medical Devices).
Virtual reality is another essential tool in diagnostics.
VR can be used to simulate different situations and track factors such as eye movement, voice, heart rate, and head rotation. This data can then be analyzed by AI algorithms to predict and diagnose various medical conations such as mental health disorders, epileptic seizures, and more.
Medical and health-related data can also be tracked outside of virtual reality to be analyzed by artificial intelligence tools in predictive medicine. For example, new innovations have led to retina scans that can detect the chance of a heart attack, Alzheimer’s, and cancer. These retina scans are relatively cheap and can be performed during a routine eye exam or in the future by our personal mobile devices.
Additionally, voice analysis can be used to detect speech patterns that are indicative of different diseases such as PTSD, dementia, or heart disease.
Once the predictions and diagnostics are complete, AI systems can be used for therapeutics. For example, virtual reality can be used to treat some mental health disorders by using exposure therapy. Many of these technologies are performed by specialists in hospitals or medical centers; however, the technology continues to become more accessible and can be programmed into at-home medical devices for patient use.
Retina scans and voice detection can now be performed on smartphones through mobile apps, and big companies such as Google are already in this game.
We are also starting to see this with the rise in popularity of wearable medical devices which can track factors such as movement, heart rate, and sleep.
Some limitations must be accounted for before these products/devices become more mainstream such as creating user-friendly systems and higher security for patient data.
Trends and Forecasts in the E-Health industry
The E-Health field has already seen an immense increase in growth and popularity since the start of COVID-19. As the world was forced to change, the E-Health field adjusted quickly and began innovating to solve problems. This push to promptly shift the healthcare industry caused the field to advance overnight in ways that otherwise would have taken years to accomplish.
The world has not only become more comfortable with the use of everyday technology, but many prefer contactless options, even when it comes to healthcare.
Additionally, E-Health options can be more affordable than traditional medicine, as it eliminates many labor aspects of the industry. Because of this, E-Health options will continue to rise in popularity as more funding goes into the E-Health and digital health research and the development of different health products that can help with diagnostics, treatments, and cures.
As the industry continues to grow, developers need to keep in mind the mandatory regulatory requirements to achieve in order to sell these digital health solutions in the markets.
These E-Health regulatory requirements include milestones such as:
- Quality Management System establishment
- Risk Analysis
- Clinical evaluation and validation
- Information security management system
- Verification & Validation (V&V)
Without FDA approval or CE in the Eu. Markets, the E-Health tools cannot be marketed to the public.