What is augmented reality?
Augmented reality (AR) combines our existing and well-known reality with virtual reality by adding virtual elements to what the user sees in real life.
For example, a user can wear a headset or view a screen to view the room they are currently in, and elements such as furniture or plants can be added to the display.
Augmented reality is a fast-growing field, and new uses are being discovered every day, and even Facebook investing big money in creating its Metaverse project.
A very promising and exciting use for augmented reality is within the E-Health industry. Augmented reality is a powerful tool for physicians as it allows them to diagnose, plan and treat patients.
About the E-Health industry
The Covid-19 pandemic has reshaped every aspect of our lives from our education system to social interactions, but nothing has seen as much growth as the medical field.
From the start of the pandemic, E-health had a major rise in popularity since people who were sick or injured still needed to be seen by doctors but wanted to avoid going in person to avoid the coronavirus.
Telemedicine is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to innovations in E-health.
Artificial intelligence and virtual reality have redefined how we can diagnose and treat patients, and we have only scratched the surface of what these technologies can do.
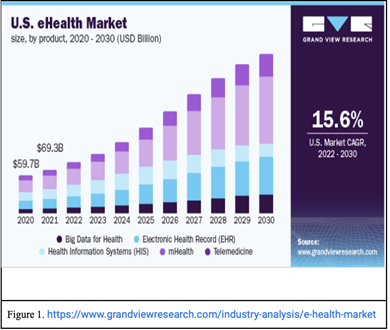
As seen in Figure 1, the US E-health market was valued at $69.3 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow rapidly with a CAGR of 15.6% by the year 2030.
With the popularity of contactless options in the wake of the pandemic, the E-Health field has ample opportunity to expand and grow in the coming years.
Medical applications using augmented reality
Augmented reality has many uses when it comes to surgeries related activities, such as:
- Physician’s training
- Surgery planning
- Exercising toward complicated surgery
- Medical treatments
- Performing these surgeries remotely
The history of robotic surgery dates back to the 1980s; however, the most popular robotic surgery system was invented in the 2000s: the Da Vinci surgical system. This robotic surgical system allows doctors to control robotic arms to perform extremely precise procedures.
The Da Vinci medical robotic system
The Da Vinci robotic system uses a camera and robotic arms on the patients and displays the image to the doctor where they can use a video-game-like system to control the robot arms. Typically, the doctors performing the surgery are on-site; however, the Da Vinci system allows surgeons to be completely remote and can perform surgeries from across the world.
Augmented reality also allows doctors across the world to guide surgeons that are on-site with the patients. With the use of surgical cameras and a display, experienced surgeons can draw and point on the display exactly where the performing surgeon should make incisions or inspect. This method is referred to as remote surgery and allows for complicated surgeries to be performed by less experienced surgeons.
The ability to perform surgeries remotely opens the door to accessible and safe healthcare for countries that do not typically have it. As long as the hospitals can set up Da Vinci or similar systems, doctors can control the robot remotely to perform the surgery.
Robotic systems for medical treatments
Robotic surgical systems allow doctors to perform precise surgeries in the operating room. It has been shown that augmented reality surgical navigation systems are well above industry accuracy standards, according to a study conducted in May 2020, “A technical accuracy at the bone entry point of 0.48 ± 0.44 mm and 0.68 ± 0.58 mm was achieved in the axial and sagittal views, respectively. The corresponding angular errors were 0.94 ± 0.83° and 0.87 ± 0.82°. The accuracy was statistically superior (p < 0.001) to ARSN without robotic assistance. Simulated pedicle screw grading resulted in a clinical accuracy of 100%.”
Robotic surgical systems have been proven to perform accurate and precise movements when used in the operating room. This advancement in robotics will allow for immense growth in the robotic surgical field as it will allow patients to receive safe and effective surgeries.
The future of the E-Health world using augmented reality
These technologies open up the door to a future where everyone will be able to have accessible health care.
Using augmented reality in surgery is just the start of how it can be used in the medical field.
It is likely that in the future augmented reality will also be able to be used for everyday medical needs such as yearly physicals or sick checkups.
With the use of cameras and displays, doctors may be able to consult patients from inside their homes. We are already seeing this with the use of telemedicine, and augmented reality can advance this field for more complicated cases.
Financial consideration using robotic and AR systems in the medical and the E-Health fields
While there is a bright future for robotic surgery, the costs of robotic systems are high, which poses a challenge to the field’s growth. A study done in 2017 suggests that each robotic procedure costs the hospital about $3.5k, including costs for instruments, accessories, robot systems, and service contracts. However, this figure only includes the manufacturer’s cost and neglects the hospital’s training and labor costs.
The instruments and robotic system account for well over half of this cost, which differs from traditional operating room costs, where instruments typically account for less than 20% of total surgery cost. This discrepancy causes robotic surgeries to cost more than traditional surgery, which has been a significant point of critique from industry professionals when it comes to robotic surgeries.
The high price tag of robotic surgeries creates a large inequality gap between patients who can and cannot afford these surgeries. This decreases the accessibility of the product and the life-saving procedures that can be performed.
Despite the high cost to hospitals, companies like Intuitive, the manufacturer of the Da Vinci system, continue to skyrocket.
According to Nature Index, “Intuitive’s stock price [grew] 66% from US $312 in 2017 to $520 in 2019. Its total revenues [grew] from $3.7 billion in 2018 to $4.5 billion in 2019 (preliminary).” While the surgery may cost more, it yields high power in being less invasive than traditional surgery, saving patients time and money in recovery. Hopefully, as the technology continues to improve, the price of instruments can decrease and become more accessible to patients everywhere.
Global Market Insights states, “Surgical Robots Market size surpassed USD 5.2 billion in 2021 and is expected to witness 17.6% CAGR from 2022 to 2030.” This suggests a great opportunity for growth within the field as more technologies gains FDA approval.
Robotic systems and AR devices FDA Approval
Robotic systems and augmented reality tools are considered medical devices in terms of regulation. It must meet all relevant regulatory requirements, such as:
- Design Control
- Technical file
- Risk Analysis
- Clinical Studies and Evaluation
- Verification & Validation
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Information and Cyber Security (ISMS)
- Patient confidentiality
The device should be submitted to the relevant health authorities such as the FDA and CE mark for registration to receive marketing approval.
The FDA has approved many robotic surgical systems after rigorous testing and research.
To gain FDA approval, surgical systems must undergo rigorous testing and show low malfunction rates, safety, and efficacy, which are better than traditional surgeries.
The FDA also continues to investigate injuries and deaths that may be due to robotic devices. However, it is hard to identify if the robotic systems are ultimately responsible for these incidents.
Public Reaction to AR and Robotic Systems in hospitals
As with all new technology, robotic-assisted surgery was met with hesitation by the public, but as technologies have improved over time, the public has begun to trust robotic surgery.
Over time, testing has shown robotic surgery to be safe, effective, and less invasive than traditional surgery. Especially in the wake of COVID-19, patients have been more welcoming to the idea of E-health in general, including the use of robotics in surgery.
Summary
The use of augmented reality in the E-health industry holds great potential as it can be used in a variety of different scenarios. Currently, augmented reality can be used by physicians to perform surgeries both robotically and by remotely guiding surgeries. Looking towards the future, there is potential for expansion for at-home use to help doctors and patients communicate and provide treatment for patients.